What Is the Main Goal of Generative AI in Tech Today?
Updated on : 25 April 2025

Image Source: google.com
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. What is Generative AI ?
- 3. Historical Evolution and Milestones
- 4. Core Technologies Behind Generative AI
- 5. Architecture of Generative AI Models
- 6. Training and Fine-tuning Methods
- 7. Evaluation Metrics and Techniques
- 8. Real-World Applications
- 9. Ethical Considerations and Challenges
- 10. Best Practices for Implementation
- 11. Leading Tools and Platforms
- 12. Future Outlook and Innovations
- 13. FAQs
Table Of Contents
Introduction
🤖✨ Imagine an AI that can write stories 📖, paint art 🎨, compose music 🎵, or even code 💻—that’s Generative AI! It learns from data and creates fresh, original content, blending creativity with technology to power the next wave of smart, imaginative tools.
What is Generative AI ?
Image Source: google
- 🔍 What is Generative AI?
- AI that creates new content rather than just analyzing.
- Learns patterns from training data and generates similar outputs.
- 🧠 How Does It Work?
- Uses deep learning models like:
- GANs (🌀) – Two networks compete to produce realistic outputs.
- VAEs (🔗) – Encode and decode data into a latent space for generation.
- Transformers (⚙️) – Use attention mechanisms for powerful sequence generation (e.g., GPT).
- 🛠️ Key Applications
- Text Generation ✍️ – Articles, stories, chats.
- Image Creation 🖼️ – Art, photos, designs.
- Music Composition 🎶 – Melody and sound generation.
- Synthetic Data Generation 📊 – For training other AI models.
- 🌟 Benefits
- Automates creative tasks.
- Enhances productivity in design, writing, and media.
- Useful in simulations and prototyping.
- ⚠️ Challenges
- Risks of bias, misuse (like deepfakes), and ethical concerns.
- High computational cost.
Historical Evolution and Milestones
-
1950s – Birth of AI 🤖
Alan Turing proposes the concept of machines mimicking human intelligence—laying the foundation for AI. -
1960s–70s – Early Neural Networks 🧠
Perceptrons and simple neural models are developed, sparking early interest in machine learning. -
1980s – Backpropagation Breakthrough 🔁
The backpropagation algorithm makes training deeper neural networks more practical. -
1990s – Probabilistic Models Rise 📊
Techniques like Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) enable early generative tasks like speech recognition. -
2014 – GANs Revolutionize Generation 🌟
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) introduced by Ian Goodfellow enable realistic image and data generation. -
2017 – Transformers Transform AI ⚡
The "Attention is All You Need" paper introduces transformers, changing the landscape of language modeling. -
2020 – GPT-3 Shocks the World 🌍
OpenAI’s GPT-3 demonstrates unprecedented natural language generation, pushing boundaries of what AI can create. -
2022+ – Multimodal & Creative AI Booms 🎨🎶
Models like DALL·E, Midjourney, and ChatGPT showcase AI’s ability to generate images, music, and code.
Core Technologies Behind Generative AI
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| 🧠 Deep Learning | A subset of machine learning using neural networks with many layers, enabling models like GPT and DALL-E to generate text and images. |
| 📊 Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Techniques for processing and understanding human language, crucial for tasks like text generation, translation, and summarization. |
| 🔢 Transformers | A deep learning model architecture that processes sequential data in parallel, powering modern NLP models like GPT, BERT, and T5. |
| 🧑💻 Large Language Models (LLMs) | Models trained on vast amounts of text data to generate human-like text, enabling applications like chatbots and content creation. |
| 🎨 Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) | A framework involving two neural networks (generator and discriminator) to create realistic images, videos, and more. |
| 📚 Reinforcement Learning | A learning paradigm where an agent learns by interacting with the environment and receiving feedback, often used in training AI for decision-making. |
| 🛠️ Transfer Learning | Using pre-trained models on new tasks, enabling efficient fine-tuning for specialized generative applications with less data. |
| ⚙️ Autoencoders | Neural networks used for unsupervised learning, particularly in image generation and data compression tasks. |

Need a AI Expert for development ?
Architecture of Generative AI Models

Image Source: google
| Architecture | Description |
|---|---|
| 🧠 Neural Networks | Algorithms modeled after the brain to learn from data. |
| 🔄 Encoder-Decoder | Encodes input data and decodes it to generate output. |
| ⚙️ Transformer | Uses attention mechanisms for efficient sequence processing. |
| 🌀 GANs | Two networks (generator and discriminator) create realistic data. |
| 🔗 VAEs | Generates new data by encoding and decoding into a latent space. |
| 🧑💻 RNNs | Processes sequential data like text or speech. |
| 🏗️ Multi-Stage Networks | Generates and refines data in multiple stages. |
| 🛠️ Attention | Focuses on important parts of the input for better context understanding. |
Empower Your Business with AI/ML Solutions with Hexadecimal Software
Training and Fine-tuning Methods
- Training Generative Models
- Learn Data Distribution: The model learns the patterns in data to generate similar outputs.
- Unsupervised Learning: No labels are required; models learn from raw data (e.g., GANs, VAEs).
- Optimization: The model is trained to reduce errors, often using loss functions.
- Fine-tuning Generative Models
- Pre-trained Models: Fine-tuning starts with a model trained on large data and adapts it for specific tasks or domains.
- Transfer Learning: The model is adapted from a general dataset to a smaller, specific one.
- Task Specialization: Fine-tuning helps improve model performance for specific tasks (e.g., text or image generation).
- Challenges
- Data Quality: Poor or biased data can affect results.
- Overfitting: Fine-tuning may cause the model to perform poorly on new data.
- High Costs: Training and fine-tuning require significant computational resources.
- Applications
- Text, Image, Audio Generation: Used in creating content like art, music, or articles.
- Synthetic Data: Helps create data for training other AI models when real data is unavailable.
Evaluation Metrics and Techniques
| Metric/Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| FID (Fréchet Inception Distance) | Measures similarity between generated and real images. |
| IS (Inception Score) | Evaluates the diversity and quality of generated images. |
| BLEU (Bilingual Evaluation Understudy) | Measures the quality of machine-generated text by comparing n-grams with reference text. |
| Perplexity | Measures how well a language model predicts a sample, often used in text generation. |
| Human Evaluation | Involves humans rating the quality and realism of generated data. |
| LPIPS (Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity) | Compares perceptual similarity between generated and real images. |
| Precision & Recall | Evaluates how many relevant samples are generated (precision) and how many relevant samples are retrieved (recall). |
| Mean Squared Error (MSE) | Measures the difference between generated data and real data, often used in image or signal generation. |
Transform Your Business with Hexadecimals Software Blockchain Expertise
Real-World Applications
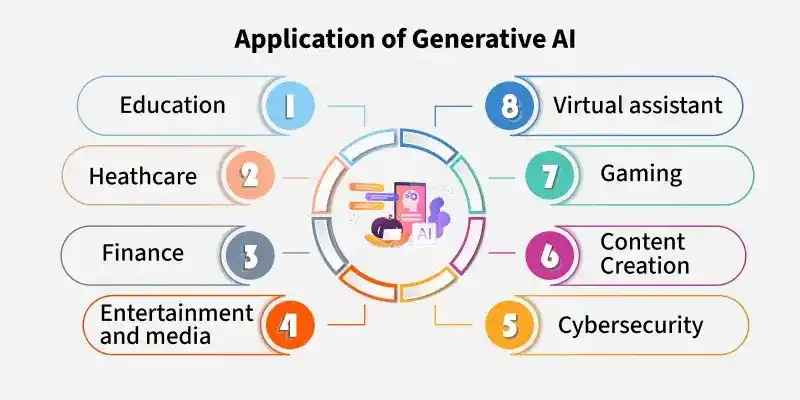
Image Source: google
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| 🖼️ Image Generation | Creates realistic images, art, and design. |
| ✍️ Text Generation | Generates articles, poetry, and stories. |
| 🎶 Music Creation | Composes music and sound effects. |
| 🦠 Drug Discovery | Generates molecular structures for new drugs. |
| 🎮 Game Content | Generates game environments, characters, and levels. |
| 💡 Product Design | Assists in designing new products and prototypes. |
| 🖥️ Code Generation | Generates code snippets or entire programs. |
| 🔍 Data Augmentation | Creates synthetic data for training AI models. |
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
| Ethical Consideration/Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Bias in Data | Generated outputs may reflect biases in training data, leading to unfair results. |
| Misinformation | Generative AI can be used to create misleading or fake content. |
| Copyright Issues | AI-generated content may infringe on existing intellectual property. |
| Job Displacement | Automation of creative tasks may impact jobs in certain industries. |
| Privacy Concerns | Generative AI may inadvertently leak private or sensitive information. |
| Security Risks | Malicious use of generative models to create harmful content, such as deepfakes. |
| Lack of Accountability | Difficult to assign responsibility for actions taken by AI systems. |
| Environmental Impact | Training large generative models can consume substantial computational resources. |
Best Practices for Implementation
- Data Quality and Preparation
- Curate Diverse and Representative Data: Ensure the training data covers a wide range of scenarios to avoid bias.
- Data Preprocessing: Clean the data, remove inconsistencies, and normalize it to improve model performance.
- Augment Data: Use data augmentation techniques to increase the variety of inputs and help the model generalize better.
- Model Selection and Customization
- Choose the Right Architecture: Depending on the task, select the appropriate generative model (e.g., GANs, VAEs, transformers).
- Fine-Tune Pre-trained Models: Utilize pre-trained models and fine-tune them to specific domains or tasks for efficiency.
- Experiment with Hyperparameters: Adjust hyperparameters like learning rate, batch size, and network layers to optimize model performance.
- Regularization and Overfitting Prevention
- Use Regularization Techniques: Implement dropout, batch normalization, or other regularization methods to prevent overfitting.
- Early Stopping: Monitor the model’s performance on validation data and stop training when performance plateaus to avoid overfitting.
- Ethical and Responsible AI
- Ensure Fairness: Check that the model does not reinforce harmful biases or unfair outcomes.
- Transparency: Make the model’s workings understandable to users and stakeholders to promote trust.
- Content Monitoring: Set guidelines to prevent harmful or unethical content generation (e.g., deepfakes, hate speech).
- Evaluation and Testing
- Use Multiple Evaluation Metrics: Implement various metrics (e.g., FID, IS) to assess the quality and diversity of generated outputs.
- Human-in-the-loop Evaluation: Include human judgment to assess the realism and relevance of the generated content.
- Continuous Testing: Regularly test and monitor the model’s output to ensure it remains aligned with goals and ethical guidelines.
- Scalability and Performance Optimization
- Optimize Computational Resources: Utilize efficient hardware (e.g., GPUs) and optimize the model to reduce computational costs.
- Scalability: Design the system to scale efficiently with increasing data and complexity while maintaining performance.
- Security and Privacy
- Data Privacy: Ensure that the model doesn’t inadvertently leak private or sensitive information during generation. 8- Security Measures: Guard against adversarial attacks, such as those that might manipulate the model’s output.
- Feedback Loop and Continuous Improvement
- Iterate Based on Feedback: Collect feedback from users and stakeholders to continuously improve the model.
- Update the Model Regularly: Re-train and fine-tune the model as new data becomes available to keep it up-to-date.

Want to build AI solutions? Reach out to us!
Leading Tools and Platforms

Image Source: google
| Tool/Platform | Description |
|---|---|
| TensorFlow | Open-source framework for deep learning and generative models. |
| PyTorch | Flexible deep learning library for generative models. |
| Hugging Face | Platform for pre-trained NLP models and easy fine-tuning. |
| OpenAI GPT | Generative model for text generation and NLP tasks. |
| RunwayML | Creative toolkit for building generative models in media. |
| DeepArt | AI platform for generating and styling images. |
| DALL·E | Generates images from text descriptions. |
| Artbreeder | Platform for creating and editing images with GANs. |
| Google Colab | Cloud platform for training AI models with free GPU access. |
| NVIDIA GANverse3D | Generates 3D models from 2D images using GANs. |
Future Outlook and Innovations
| Future Outlook/Innovation | Description |
|---|---|
| AI Creativity 🎨 | Generative AI will enable advanced creative tasks, including music, art, and writing. |
| Multimodal Models 🌐 | AI models will combine text, images, audio, and video for richer content generation. |
| Improved Ethics and Safety 🛡️ | Enhanced safeguards will prevent harmful or biased content generation. |
| Self-Supervised Learning 🤖 | Models will learn with minimal supervision, improving efficiency. |
| Personalized AI 👤 | Generative AI will cater to individual user preferences and needs. |
| AI in Healthcare 🏥 | Generative AI will assist in drug design, diagnostics, and personalized treatments. |
| Quantum Computing ⚛️ | Quantum advancements will allow generative AI to process complex data. |
| AI in Gaming 🎮 | AI will create dynamic and immersive game worlds and characters. |
| Real-Time AI Generation ⏱️ | Generative AI will enable real-time content generation for interactive applications. |
| Autonomous AI 🤖 | Generative AI models will operate with greater autonomy across various industries. |
FAQs
Q.1. What is the goal of Generative AI?
A: The goal is to create new, realistic data (images, text, audio, etc.) by learning patterns from existing data.
Q.2. How does Generative AI work?
A: It uses machine learning models like GANs, VAEs, or transformers to generate new content based on learned patterns.
Q.3. What are some common uses of Generative AI?
A: It's used for creating art, music, text, video, and synthetic data for training other AI models.
Q.4. What are the key types of Generative AI models?
A: The most common models include GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), VAEs (Variational Autoencoders), and transformers.
Q.5. What are the benefits of Generative AI?
A: It can automate creative processes, generate synthetic data for training, and produce innovative solutions in various industries.
Q.6. What challenges does Generative AI face?
A: Challenges include data bias, overfitting, ethical concerns, and the need for high computational resources.
Q.7. Is Generative AI ethical?
A: It can be ethical if used responsibly, but there are concerns about misuse for creating fake content or deepfakes.

