Inter Process Communication in Operating Systems
Updated on : 11 April 2025
Image Source: google.com
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Understanding Inter-Process Communication (IPC)
- 3. Why Processes Need to Communicate
- 4. Exploring Different IPC Techniques
- 5. Typical Use Cases for IPC
- 6. Challenges and Drawbacks of IPC
- 7. Leveraging Python for Inter-Process Communication
- 8. Making Data Transfer Possible Serialization Basics
- 9. Serialization Tools in Python for IPC
- 10. Hands-On IPC Examples in Python
- 11. Tips and Techniques for Effective IPC
- 12. Wrapping Up Key Insights and Future Directions
- 13. FAQs
Table Of Contents
Introduction
Ever wondered how apps talk to each other behind the scenes? That’s IPC Inter Process Communication! It’s the secret sauce 🧪 in operating systems that lets processes share data , sync tasks , and work together smoothly 🤝.
Understanding Inter-Process Communication (IPC)
Image Source: google
- 🧠 What is IPC?
- A method that enables communication between independent processes in a system.
- 🔄 Why is IPC important?
- Helps in data sharing, process synchronization, and efficient resource utilization.
- 🛠️ Where is IPC used?
- Found in multitasking environments, client-server models, and distributed systems.
- 🧵 Processes vs Threads:
- IPC connects processes (independent), while threads often share memory directly.
- 💬 How does it work?
- Through mechanisms like message queues, shared memory, pipes, sockets, and signals.
- 🚫 Without IPC:
- Processes would work in isolation, leading to inefficiency and poor performance.
Why Processes Need to Communicate
| 🔗 Reason | 📋 Explanation |
|---|---|
| Data Sharing | Processes often need to share data to perform tasks efficiently. |
| Coordination | Helps synchronize actions between multiple processes. |
| Resource Access | Processes communicate to access shared resources safely. |
| Task Division | Enables splitting complex jobs into smaller, manageable tasks. |
Exploring Different IPC Techniques
| 🛠️ Technique | 📋 Description |
|---|---|
| Pipes | Simple, one-way communication used between related processes. |
| Message Queues | Processes send and receive messages via a managed queue. |
| Shared Memory | Processes access a common memory space for fast data exchange. |
| Sockets | Used for communication between processes on the same or different machines. |
| Signals | Used to notify processes about events or trigger specific actions. |

Optimize Your Systems with IPC-Driven Solutions from Hexadecimal Software
Typical Use Cases for IPC
Image Source: google
- Client-Server Applications
- IPC allows the client and server to exchange data efficiently in real-time systems and networked applications.
- Multitasking in Operating Systems
- Enables communication and coordination between background services and active applications.
- Parallel and Distributed Computing
- Helps break down large computations into smaller tasks handled by multiple processes working together.
- Real-Time Embedded Systems
- Used in robotics, automotive systems, and IoT for instant and synchronized inter-process communication.
- Web Applications & E-commerce Platforms
- Microservices and backend modules interact through IPC for tasks like authentication, payment processing, and user management.
Challenges and Drawbacks of IPC
- Complex Synchronization
- Ensuring that processes access shared resources without conflicts requires careful synchronization mechanisms like locks and semaphores.
- Security Risks
- Improper IPC implementation can expose sensitive data or allow unauthorized access between processes.
- Performance Overhead
- Some IPC methods (like message passing or networked sockets) introduce latency and CPU overhead due to context switching and data handling.
- Debugging Difficulty
- Tracking bugs in IPC-based systems can be complex, especially with race conditions and interdependent processes.
- Scalability Limitations
- As the number of communicating processes grows, managing IPC channels and ensuring efficient communication becomes harder.
- Platform Dependency
- Some IPC mechanisms work differently across operating systems, making portability a challenge in cross-platform applications.
Leveraging Python for Inter-Process Communication
| 🐍 Feature | 📋 Description |
|---|---|
| multiprocessing | Provides support for spawning processes using an API similar to threading. |
| Queue & Pipe | Used for safe communication between Python processes with built-in support. |
| shared_memory | Allows multiple processes to access and modify shared memory space. |
| socket | Supports network and local communication between processes via sockets. |
| subprocess | Allows running external programs and communicating with them via input/output pipes. |
Making Data Transfer Possible Serialization Basics
| 🔑 Concept | 📋 Description |
|---|---|
| Serialization | Converts objects into a transferable format like bytes or text. |
| Deserialization | Rebuilds objects from serialized data for use in a program. |
| Purpose | Allows structured data to be shared between processes or systems. |
| Common Formats | JSON, Pickle, XML, Protocol Buffers, MessagePack, etc. |
| Use in IPC | Serialized data enables communication through sockets, pipes, etc. |
Serialization Tools in Python for IPC
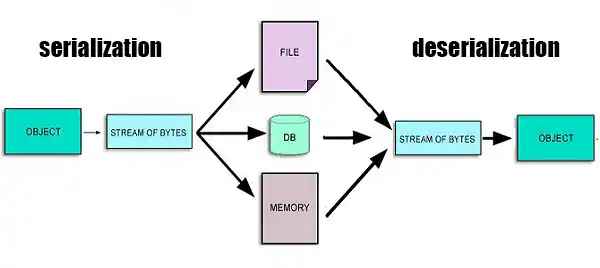
Image Source: google
pickle🧂
- Python's built-in module for serializing and deserializing Python objects.
- Supports complex objects, custom classes, and is easy to use.
- Limitation: Not secure against untrusted data.
json📄
- Standard for serializing data into a readable text format.
- Interoperable with most languages.
- Ideal for simple data types (dict, list, string, etc.).
- Limitation: Doesn’t support custom or complex Python objects directly.
marshal⚙️
- Lower-level serialization module used internally by Python.
- Fast but limited to basic Python types.
- Limitation: Not intended for general use; version-dependent.
MessagePack📦 (third-party)
- Binary format that is faster and smaller than JSON.
- Good for performance-critical applications.
- Cross-language support.
protobuf(Protocol Buffers) 📑 (third-party)
- Developed by Google for high-performance serialization.
- Requires defining message structures via
.protofiles. - Excellent for large-scale and distributed systems.
Hands-On IPC Examples in Python
Image Source: google
- Using
multiprocessing.Queue
- Allows safe, FIFO-based communication between Python processes.
- Example: Passing tasks or results between worker processes.
- Using
Pipe
- Simple two-way connection for sending data between two processes.
- Great for direct communication.
- Shared Memory with
multiprocessing.shared_memory
- Enables multiple processes to access and modify a shared data buffer.
- Useful for high-speed data transfer (e.g., image processing).
- Using
socketfor IPC over a network or localhost
- Set up server-client architecture for data exchange.
- Works across machines or locally.
- Using
subprocessto communicate with external processes
- Run and interact with external programs through standard input/output.
Web App Development Services with Hexadecimal software Expertise
Tips and Techniques for Effective IPC
| ✅ Tip | 📋 Description |
|---|---|
| Use the Right IPC Method | Choose IPC technique (e.g., Queue, Pipe, Socket) based on the use case and performance needs. |
| Keep Data Formats Simple | Use simple, consistent data formats like JSON for easier serialization and debugging. |
| Avoid Deadlocks | Design communication flow carefully to prevent processes from waiting on each other indefinitely. |
| Use Synchronization Primitives | Leverage locks, semaphores, or events to manage shared resources safely. |
| Test and Debug Thoroughly | Simulate communication under various conditions to catch issues like race conditions or data loss. |

Build High-Performance Apps with Efficient IPC Techniques
Wrapping Up Key Insights and Future Directions
| 🔍 Insight / Direction | 📋 Description |
|---|---|
| IPC is Essential | IPC is a backbone of modern OS and software systems, enabling process collaboration and resource sharing. |
| Choose Wisely | Different IPC methods serve different needs—understand your use case before selecting one. |
| Python Makes It Easy | Python’s built-in libraries simplify IPC implementation for developers at all levels. |
| Security Matters | Implement security best practices when sharing data between processes or over networks. |
| Future Trends | Expect more use of IPC in cloud-native apps, microservices, and AI workloads requiring high concurrency. |
FAQs
Q.1. What is Inter-Process Communication (IPC)?
A : IPC is a mechanism that allows processes to exchange data and signals with one another, enabling coordination and resource sharing.
Q.2. Why is IPC needed in operating systems?
A : It enables processes to collaborate, share data, coordinate actions, and manage shared resources efficiently.
Q.3. What are the main IPC mechanisms?
A : Pipes.
A : Message Queues.
A : Shared Memory.
A : Sockets.
A : Signals.
A : Semaphores.
Q.4. What is the difference between shared memory and message passing?
A : Shared Memory Processes access a common memory area; fast but needs synchronization..
A : Message Passing Processes communicate by sending/receiving messages; easier but slower.
Q.5. Is IPC used only within one system?
A : IPC can be local (within the same system) or remote (between systems over a network using sockets, RPC, etc.).
Q.6. What is a real-world example of IPC?
A : A web browser rendering a page while downloading content uses multiple processes that communicate via IPC.
Q.7. Which programming languages support IPC?
A : Most modern languages like Python, C, Java, and Go offer IPC support through libraries and system calls.
Q.8. What are the challenges of IPC?
A : Common challenges include synchronization issues, data consistency, security risks, and debugging complexity.

